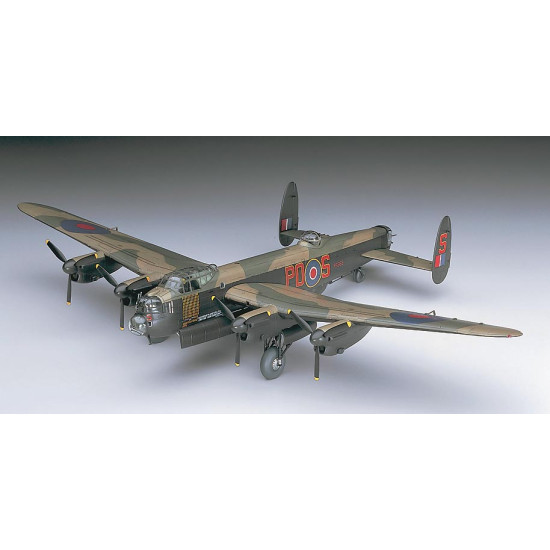
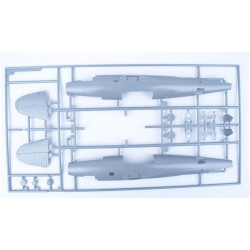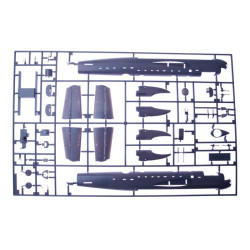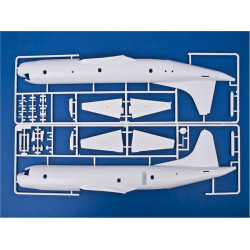






Lancaster B Mk.III "Dambusters"
1/72 Aircrafts, Planes
Hasegawa 00554
Manufacturer: Hasegawa
Scale: 1/72
Material: Plastic
Paint: Unpainted, Unassembled, Kit do not contain paints and glue.
Condition: New in Box
The Avro Lancaster is a British four-engined Second World War heavy bomber designed and built by Avro for the Royal Air Force (RAF). It first saw active service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942 and, as thestrategic bombing offensive over Europe gathered momentum, it became the main heavy bomber used by the RAF, the RCAF, and squadrons from other Commonwealth and European countries serving within the RAF, overshadowing its close contemporaries the Handley Page Halifax and Short Stirling.The Lancaster, an evolution of the troublesome Avro Manchester, was designed by Roy Chadwick and was powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins, or, in one version, Bristol Hercules engines.A long, unobstructed bomb bay meant that the Lancaster could take even the largest bombs used by the RAF, including the 4,000 lb (1,800 kg), 8,000 lb (3,600 kg), and 12,000 lb (5,400 kg) blockbusters, loads often supplemented with smaller bombs or incendiaries. The versatility of the Lancaster was such that it was chosen to equip 617 Squadron, and was modified to carry the Barnes Wallis designedUpkeep "Bouncing bomb" for Operation Chastise, the attack on Germany's Ruhr Valley dams. Although the Lancaster was primarily a night bomber, it excelled in many other roles, including daylight precision bombing: in the latter role some Lancasters were adapted to carry the 12,000 lb (5,400 kg) Tallboy and, ultimately, the 22,000 lb (10,000 kg)Grand Slam earthquake bombs (also designed by Wallis).As early as 1943, a Lancaster was converted to become an engine test bed for the Metropolitan-Vickers F.2 turbojet. Lancasters were later used to test several different engines, including the Armstrong Siddeley Mamba and Rolls-Royce Dart turboprops, and the Avro Canada Orendaand STAL Dovern turbojets. Postwar, the Lancaster was supplanted as the RAF's main strategic bomber by the Avro Lincoln, itself a larger permutation of the Lancaster. Instead the Lancaster took on the role of long range anti-submarine patrol aircraft (later supplanted by the Avro Shackleton) and air-sea rescue. It was also used in roles as diverse as photo-reconnaissance and aerial mapping, as a flying tanker for aerial refueling, and as the Avro Lancastrian, a long-range, high-speed transatlantic passenger and postal delivery airliner. In March 1946, a Lancastrian of BSAA flew the first scheduled flight from the then new London Heathrow Airport.ome of the later orders for Manchesters were changed in favour of Lancasters; the designs were very similar and both featured the same distinctive greenhouse cockpit, turret nose, and twin tail. The Lancaster discarded the stubby central third tail fin of the early Manchesters and used the wider span tailplane and larger elliptical twin fins from the later Manchester IA.
The Lancaster is a mid-wing cantilever monoplane with an oval all-metal fuselage. The wing was constructed in five main sections, the fuselage in five sections. All wing and fuselage sections were built separately and fitted with all the required equipment before final assembly. The tail unit had twin elliptical fins and rudders. The Lancaster was initially powered by four wing-mounted Rolls-Royce Merlin piston engines driving 13 ft diameter de Havilland Hydromatic three-bladed airscrews. It had retractable main landing gear and fixed tailwheel, with the hydraulically operated main landing gear raising rearwards into the inner engine nacelles.The majority of Lancasters built during the war years were manufactured by Avro at their factory at Chadderton near Oldham, Greater Manchester, and test flown fromWoodford Aerodrome in Cheshire. Other Lancasters were built by Metropolitan-Vickers (1,080, also tested at Woodford), and Armstrong Whitworth. The aircraft was also produced at the Austin Motor Company works in Longbridge, Birmingham, later in the Second World War and postwar by Vickers-Armstrongs at Chester as well as at the Vickers Armstrong factory, Castle Bromwich, Birmingham. Only 300 of theLancaster B II fitted with Bristol Hercules engines were constructed; this was a stopgap modification caused by a shortage of Merlin engines as fighter production was of higher priority. Many BIIs were lost after running out of fuel.[citation needed] TheLancaster B III had Packard Merlin engines but was otherwise identical to contemporary B Is, with 3,030 B IIIs built, almost all at Avro's Newton Heath factory. The B I and B III were built concurrently, and minor modifications were made to both marks as new batches were ordered. Examples of these modifications were the relocation of the pitot head from the nose to the side of the cockpit, and the change from de Havilland "needle blade" propellers to Hamilton Standard or Nash Kelvinator made "paddle blade" propellers.
Avro Lancaster
Royal Air Force Avro Lancaster B I PA474 of the Battle of Britain Memorial Flight. This aircraft carries the deepened bomb aimer's blister (Mod. 780), and the later paddle-bladed propellers. Neither H2Sblister nor exhaust shrouds are fitted.
Role
Heavy bomber
Manufacturer
Avro
Designer
Roy Chadwick
First flight
9 January 1941
Introduction
February 1942
Retired
1963 (Canada)
Primary users
Royal Air Force
Royal Canadian Air Force
Royal Australian Air Force
Royal New Zealand Air Force
Number built
7,377
Unit cost
£45-50,000
Developed from
Avro Manchester
Variants
Avro Lancastrian
| General Product Info | |
| Material | NOT SET |
| Scale | 1/72 |
| Type | Bomber |
We have the lowest worldwide shipping. And it's totally simple.
EUROPE, USA, CANADA TURKEY, ISRAEL, EGYPT, UE CHINA, JAPAN, HK, S.KOREA | AU NZ MX South America, Asia | |
| Order weight up to 0.22kg or 0.48lb | US$ 8.90 | US$ 8.90 |
| Order weight up to 0.44kg or 0.97lb | US$ 13.95 | US$ 17.90 |
| Order weight over 0.44kg or 0.97lb | US$ 19.99 | US$ 29.99 |
| Order total over $150 | FREE | PROMO US$ 19.99 |
Shipping to some countries not qualifies for the free shipping option but costs not over $29.99 for any sized order. Sorry for that, your location is too far.
- Stock: Out Of Stock
- Model: HA00554
- Weight: 1.12lb
- DATE ADDED: 08/04/2014










































































-250x250w.jpg)