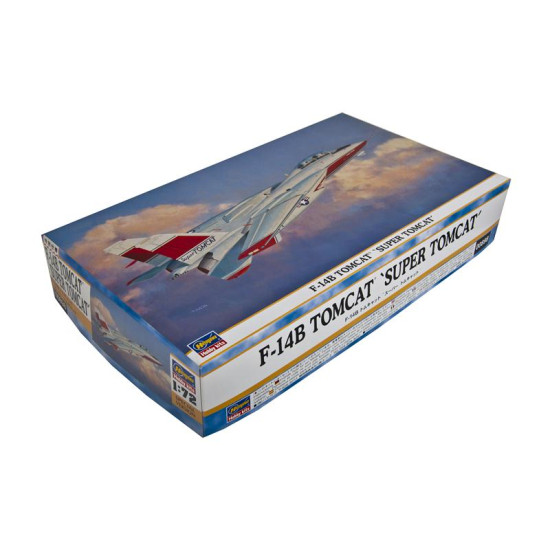
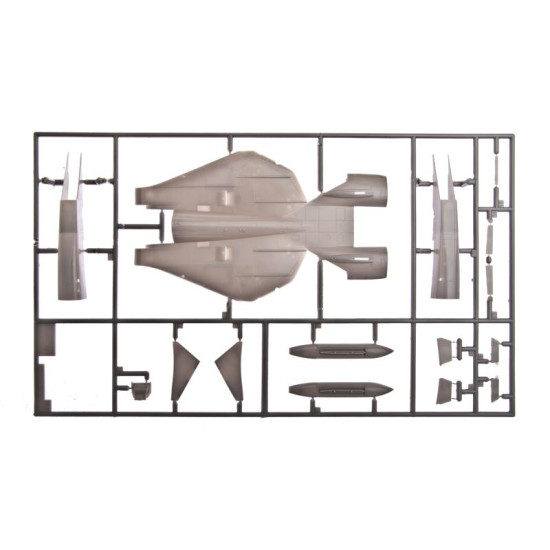
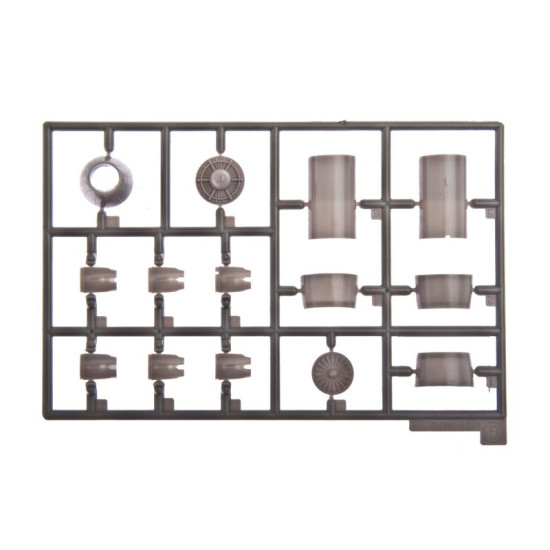
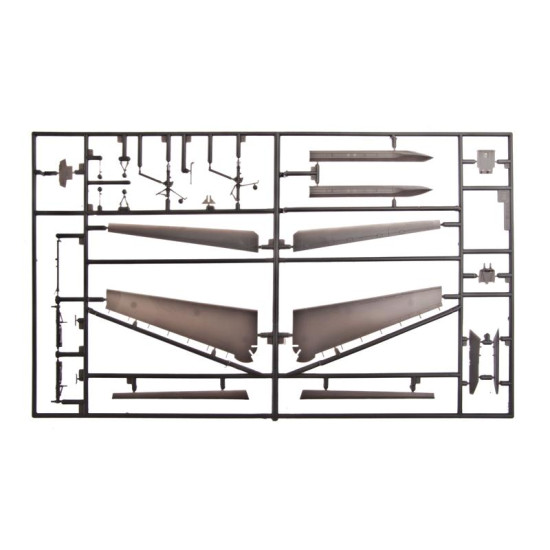
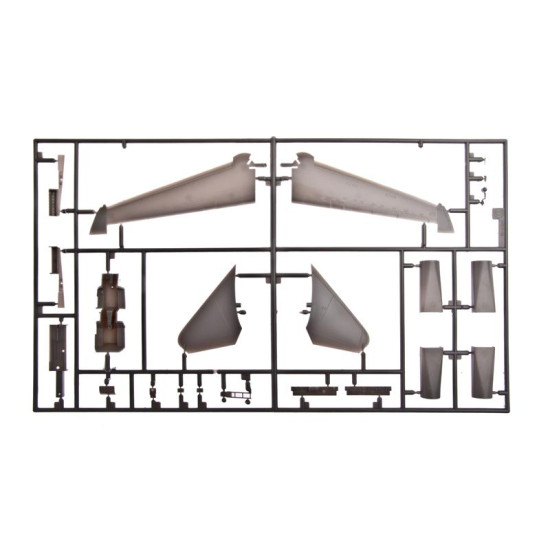




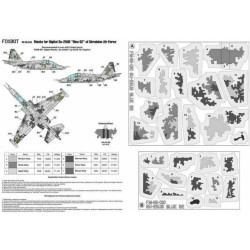
Grumman F-14 Tomcat
1/72 Aircrafts, Planes
Hasegawa 00898
Manufacturer: Hasegawa
Scale: 1/72
Material: Plastic
Paint: Unpainted, Unassembled, Kit do not contain paints and glue.
Condition: New in Box
The Grumman F-14 Tomcat is a supersonic, twinjet, two-seat, variable-sweep wing fighter aircraft. The Tomcat was developed for the United States Navy's Naval Fighter Experimental (VFX) program following the collapse of the F-111B project. The F-14 was the first of the Americanteen-series fighters which were designed incorporating the experience of air combat against MiG fighters during the Vietnam War.
The F-14 first flew in December 1970 and made its first deployment in 1974 with the U.S. Navy aboard USS Enterprise (CVN-65), replacing theMcDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II. The F-14 served as the U.S. Navy's primary maritime air superiority fighter, fleet defense interceptor and tactical reconnaissance platform. In the 1990s, it added the Low Altitude Navigation and Targeting Infrared for Night (LANTIRN) pod system and began performing precision ground-attack missions.As of 2012, the F-14 was only in service with the Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force, having been exported to Iran in 1976, when the U.S. had amicable diplomatic relations with Iran.However, weight and performance issues plagued the U.S. Navy F-111B variant for TFX and would not be resolved to the navy's satisfaction. The F-111 manufacturerGeneral Dynamics partnered with Grumman on the navy F-111B. With the F-111B program in distress, Grumman began studying improvements and alternatives. In 1966, the navy awarded Grumman a contract to begin studying advanced fighter designs. Grumman narrowed down these designs to its 303 design.Vice Admiral Thomas F. Connolly, Deputy Chief of Naval Operations for Air Warfare, took the developmental F-111A variant for a flight and discovered that it had difficulty going supersonic and had poor carrier landing characteristics. He later testified to congress about his concerns against the official Department of the Navy position and, in May 1968, congress stopped funding for the F-111B, allowing the navy to pursue an answer tailored to their requirements. The name "Tomcat" was partially chosen to pay tribute to Admiral Connolly, as the nickname "Tom's Cat" had already been widely used by the manufacturer, although the name also followed the Grumman tradition of naming its fighter aircraft after felines.Upon winning the contract for the F-14, Grumman greatly expanded its Calverton, Long Island, New York facility for evaluating the aircraft. Much of the testing, including the first of many compressor stalls and multiple ejections, took place over Long Island Sound. In order to save time and forestall interference from Secretary McNamara, the navy skipped the prototype phase and jumped directly to full-scale development; the air force took a similar approach with its F-15. The F-14 first flew on 21 December 1970, just 22 months after Grumman was awarded the contract, and reached initial operational capability (IOC) in 1973. The United States Marine Corps was initially interested in the F-14 as an F-4 Phantom II replacement; going so far as to send officers to Fighter Squadron One Twenty-Four (VF-124) to train as instructors. The marine corps pulled out of any procurement when development of the stores management system for ground attack munitions was not pursued. An air-to-ground capability was not developed until the 1990s.Firing trials involved launches against simulated targets of various types, from cruise missiles to high-flying bombers. AIM-54 Phoenix missile testing from the F-14 began in April 1972. The longest single Phoenix launch was successful against a target at a range of 110 nmi (200 km) in April 1973. Another unusual test was made on 22 November 1973, when six missiles were fired within 38 seconds at Mach 0.78 and 24,800 ft (7,600 m); four scored direct hits.The LANTIRN pod did not require changes to the F-14's own system software, but the pod was designed to operate on a MIL-STD-1553B bus not present on the F-14A or B. Consequently, Martin Marietta specially developed an interface card for LANTIRN. The Radar Intercept Officer (RIO) would receive pod imagery on a 10-inch Programmable Tactical Information Display (PTID) or another Multi-Function Display in the F-14 ear cockpit and guided LGBs using a new hand controller installed on the right side console. Initially, the hand controller replaced the RIO's TARPS control panel, meaning a Tomcat configured for LANTIRN could not carry TARPS and the reverse, but eventually a workaround was later developed to allow a Tomcat to carry LANTIRN or TARPS as needed.
F-14 Tomcat
A U.S. Navy F-14D conducts a mission over thePersian Gulf-region on November 5, 2005.
Role
Interceptor, air superiority andmultirole combat aircraft
National origin
United States of America
Manufacturer
Grumman Aerospace Corporation
First flight
21 December 1970
Introduction
22 September 1974
Retired
22 September 2006 (United States Navy)
Status
In service with the Iranian Air Force
Primary users
United States Navy (historical)
Imperial Iranian Air Force
Islamic Republic of Iran Air Force
Produced
1969-1991
Number built
712
Unit cost
US$38 million (1998)
| General Product Info | |
| Material | NOT SET |
| Scale | 1/72 |
| Type | NOT SET |
We have the lowest worldwide shipping. And it's totally simple.
EUROPE, USA, CANADA TURKEY, ISRAEL, EGYPT, UE CHINA, JAPAN, HK, S.KOREA | AU NZ MX South America, Asia | |
| Order weight up to 0.22kg or 0.48lb | US$ 8.90 | US$ 8.90 |
| Order weight up to 0.44kg or 0.97lb | US$ 13.95 | US$ 17.90 |
| Order weight over 0.44kg or 0.97lb | US$ 19.99 | US$ 29.99 |
| Order total over $150 | FREE | PROMO US$ 19.99 |
Shipping to some countries not qualifies for the free shipping option but costs not over $29.99 for any sized order. Sorry for that, your location is too far.
- Stock: Out Of Stock
- Model: HA00898
- Weight: 0.79lb
- DATE ADDED: 08/04/2014




















































































































-250x250w.jpg)